| Difference between Crystalline and Amorphous | |
|---|---|
| CRYSTALLINE SOLIDS | AMORPHOUS SOLIDS |
| Atoms are arranged in regular 3 dimension | They do not have regular arrangement |
| Sharp melting point | No particular melting point |
| Anisotropic | Isotropic |
| True solid | Pseudo solid |
| Symmetrical | Unsymmetrical |
| More rigid | Less rigid |
| Long range order | Short range order |
| Example: Potassium nitrate, copper | Example: Cellophane, polyvinyl chloride |
| Type of Solid | Atoms | Forces between particles | Properties | Examples |
| Metallic | atoms | Metallic bond | Soft to hard, low to high melting point, electrical and thermal conductivity, malleable & ductile | all metals (M.P- fairy high) |
| Molecular | atoms or molecules | Hydrogen bond, dipole-dipole, dispersion (temporary) | soft, low to moderately high melting point, poor electrical and thermal conductivity | most organic & inorganic compounds (methane, sugar, water) (M.P-low) |
| Ionic | Positive & negative ions | electrostatic attractions | Hard, brittle, high melting point, poor electrical and thermal conductivity | ionic salts (NaCl, KBr, MgSO4) (M.P-high) |
| Covalent-Network | Covalent bonds | covalent bond | very hard, brittle, very high melting point, often poor electrical and thermal conductivity | diamond, Silicon, quartz, graphite (all made from a non-metallic element) (M.P- very high) |
Unit Cells
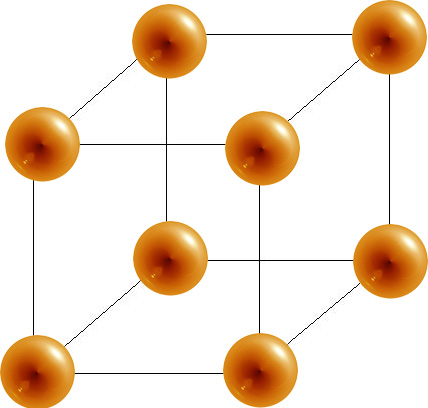
A unit cell is the smallest portion of a crystal lattice that shows the three-dimensional pattern of the entire crystal. A crystal can be thought of as the same unit cell repeated over and over in three dimensions. The Figure below illustrates the relationship of a unit cell to the entire crystal lattice.

A unit cell is the smallest repeating portion of a crystal lattice.
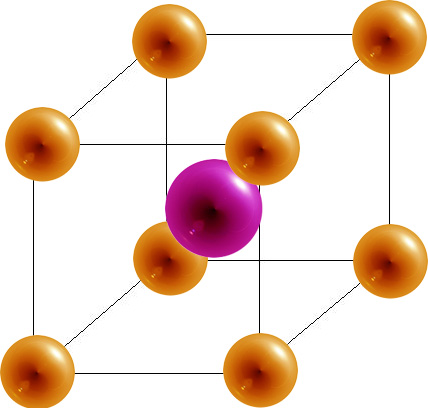
Unit cells occur in many different varieties. As one example, the cubic crystal system is composed of three different types of unit cells: (1) simple cubic , (2) face-centered cubic , and (3)body-centered cubic . These are shown in three different ways in the Figure below .

Simple Unit Cell
| 6 | 1 | 52% |
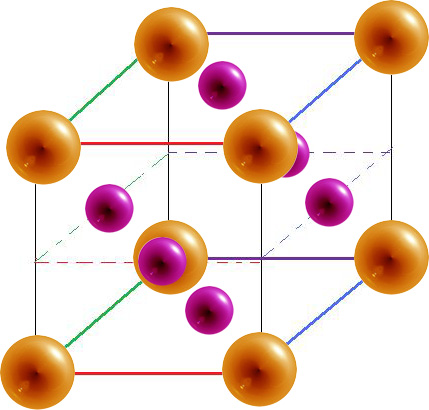
Body-Centered Cubic
| 8 | 2 | 68% |
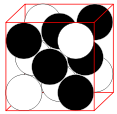
Face-centered Cubic
| 12 | 4 | 74.04% |
Cubic Closest Packed
| 12 | 4 | 74.04% |
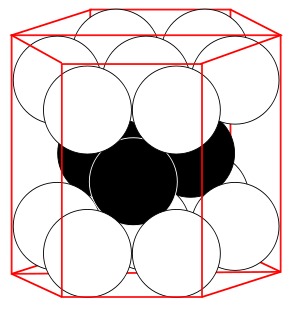
Hexagonal Closest Packed
| 12 | 6* (2) see note below | 74.04% |
vs
Void
Tetrahedral Voids are unoccupied, empty spaces present in substances having tetrahedral crystal systems. Octahedral voids are unoccupied, empty spaces present in substances having octahedral crystal systems. Crystal System Tetrahedral Voids can be found in substances having a tetrahedral arrangement in their crystal system. Octahedral Voids can be found in substances having an octahedral arrangement in their crystal system. Location in the Unit Cell Tetrahedral Voids can be observed in edges of the unit cell. Octahedral voids can be observed in the centre of the unit cell. Coordination Number The coordination number of the tetrahedral void is four. The coordination number of the octahedral void is six. Number of Voids in the Crystal Lattice There are two tetrahedral voids per sphere in the crystal lattice. There are one octahedral void per sphere in the crystal lattice.
Figure 1: Two Tetrahedral Voids.
Figure 2: An Octahedral void at the centre of the unit cell.
There are 3 types of point defects
- Stoichiometric defect
- Frenkel defect
- Schottky defect
1. Stoichiometric Defect:
In this kind of point defect, the ratio of positive and negative ions (Stoichiometric) and electrical neutrality of a solid is not disturbed. Sometimes it is also known as intrinsic or thermodynamic defects.
Fundamentally, they are of two types:
- Vacancy defect: When an atom is not present at their lattice sites, then that lattice site is vacant and it creates a vacancy defect. Due to this, the density of a substance decreases.
- Interstitial defect: It is a defect in which an atom or molecule occupies the intermolecular spaces in crystals. In this defect, the density of the substance increases.
A non-ionic compound mainly shows vacancy and interstitial defects. An ionic compound shows the same in Frenkel and Schottky defect.
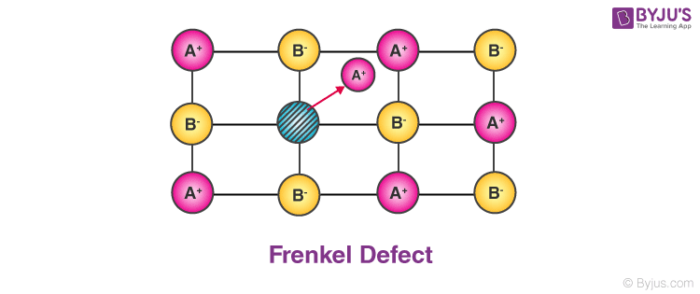
2. Frenkel Defect:
In ionic solids generally, the smaller ion (cation) moves out of its place and occupies an intermolecular space. In this case, a vacancy defect is created on its original position and the interstitial defect is experienced at its new position.
- It is also known as dislocation defect.
- The density of a substance remains unchanged.
- It happens when there is a huge difference in the size of anions and cations.
- Example: ZnS and AgCl.

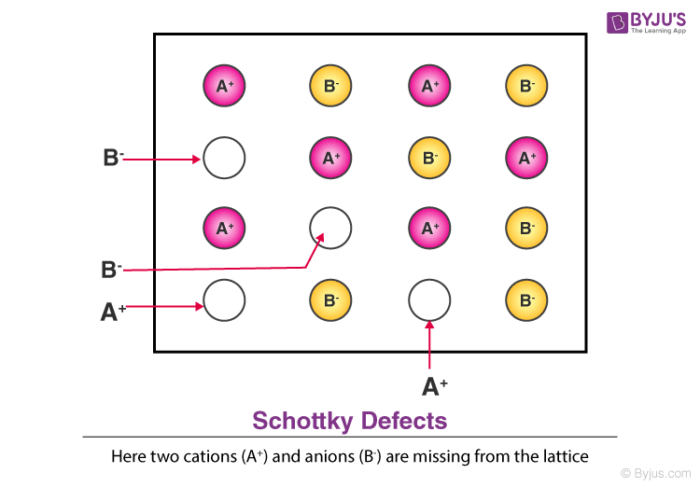
3. Schottky Defect
- This kind of vacancy defects is found in Ionic Solids. But in ionic compounds, we need to balance the electrical neutrality of the compound so an equal number of anions and cations will be missing from the compound.
- It reduces the density of the substance.
- In this, the size of cations and anions are of almost the same.
- Impurity Defect: Let’s understand the impurity defect by an example. If molten NaCl is crystallized with SrCl2 compound then the Sr2+ ions replace two Na+ ions and occupy the place of one Na+ In this way the lattice site of one Na+ is vacant and it creates an impurity defect.
- Non-Stoichiometric Defect: In this defect, the cations and anions ratio is disturbed either because of adding or removing of ions.




0 Comments